Account Preparation :
The critical work of creating financial statements, which is the ultimate goal of financial reporting and the accounting system, comes at the end of the accounting cycle.
Depending on the size of the company and other requirements, there are differences in the complexity of preparing these statements. Some claims necessitate additional footnotes and disclosures, which further accentuate the complexity and detail of the entire procedure. These statements are produced by using specific account balances from the adjusted trial balance.

Accounts Preparation for Simple Financial Statements :
Financial Statement :
A company’s financial transactions and endeavours are recorded and disclosed through the preparation of financial statements, which is a fundamental component of effective financial management.
Business Finances :
Fundamentally, financial statements offer a thorough summary of the cash flows, financial position, and fiscal performance of an organisation. These statements are essential tools that support thorough financial analysis and assist in decision-making.
A thorough understanding of accounting principles, unwavering adherence to strict standards and regulations, and an unwavering commitment to meticulousness in recording and reporting financial data are all necessary for creating accurate financial statements.
Importance of financial statements :
The process of preparing financial statements entails creating precise financial records that reflect the financial standing of an organisation. It’s important because it makes decisions easier for stakeholders, including creditors, investors, and regulators. It also ensures that accounting standards are followed and accurately depicts the company’s financial health.
Knowledge-Based Decision-Making :
Prepared financial statements provide a thorough overview of a company’s financial health, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions.Well-prepared financial statements provide stakeholders with the information required for strategic decision-making and perceptive financial assessment by providing a thorough overview of a company’s financial health.
Main elements of financial statements :
The balance sheet, income statement, statement of cash flows, and statement of stockholders’ equity are the essential components. When combined, they provide a thorough understanding of a business’s performance, cash flows, equity fluctuations, and financial status. The balance sheet and equity statement are directly impacted by the income and cash flow statements.
Financial Statement Preparation Guide :
Financial statements serve as vital documents for evaluating a company’s performance and financial health. The process of preparing these statements involves several crucial steps, ensuring accuracy and transparency for stakeholders such as management, investors, lenders, and creditors.
1. Receipt of Supplier Invoices Confirmation
Ensure all supplier invoices are accounted for by cross-referencing the receiving log with accounts payable. Any missing invoices should be accrued as expenses.
2. Issuance of Customer Invoices Verification
Cross-verify the shipping log with accounts receivable to confirm the issuance of all customer invoices. Generate pending invoices as needed.
3. Accrual of Unpaid Wages
Recognize expenses for wages earned but not yet disbursed by the end of the reporting period. Explore comprehensive courses covering the nuances of closing procedures like "Closing the Books," "The Soft Close," and "The Year-End Close."
4. Depreciation and Amortization Calculation
Compute depreciation and amortization expenses for all fixed assets based on the accounting records.
5. Inventory Valuation
Conduct an end-of-period physical inventory count or utilize alternate methods to estimate the closing inventory balance. Use this data to calculate the cost of goods sold, updating the accounting records accordingly.
6. Bank Account Reconciliation
Perform a thorough bank reconciliation, adjusting the accounting records to align with the bank statement through necessary journal entries.
7. Posting Account Balances
Transfer all subsidiary ledger balances to the general ledger for comprehensive bookkeeping.
8. Account Review
Carefully scrutinize the balance sheet accounts, making necessary journal entries to reconcile balances with supporting details.
9. Financial Statement Review
Generate preliminary financial statements and meticulously review them for discrepancies. Address any identified errors by creating corresponding journal entries, repeating the review process until accuracy is achieved.
10. Accrual of Income Taxes
Estimate and accrue income tax expenses based on the corrected income statement figures.
11. Closing Accounts
Close all subsidiary ledgers for the reporting period while preparing them for the subsequent period.
12. Distribution of Financial Statements
Finalize and print the financial statements. Craft accompanying footnotes to elucidate critical points within the statements. Draft a cover letter outlining key aspects of the financial statements. Assemble these documents into packets for distribution to intended recipients
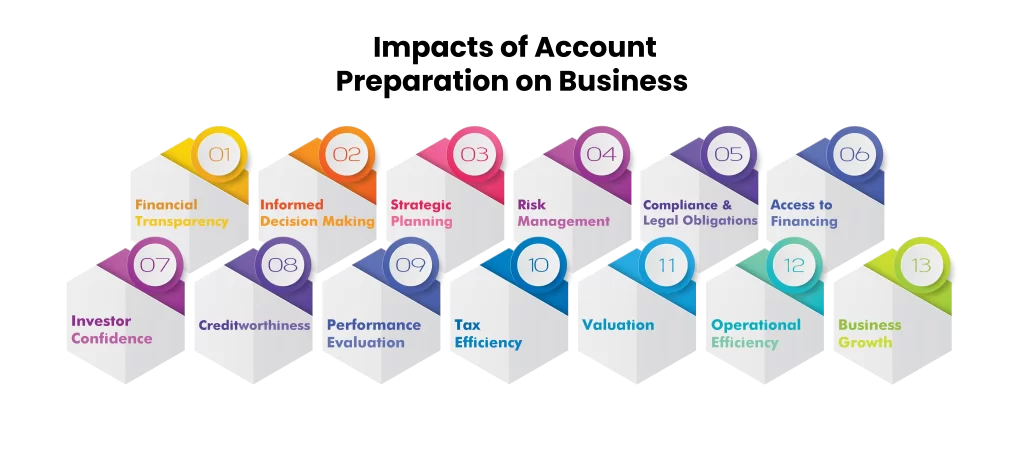
Basic Principles for peparing Financial Statements :
Accrual accounting is essential to the preparation of financial statements because it records transactions immediately, regardless of monetary exchanges. This approach guarantees a more realistic representation of a business’s financial situation by emphasising the timing of economic events rather than cash movements.
Importance in Revealing
In accounting, materiality measures the significance of data or transactions. Any item considered material has the ability to affect users' decisions based on financial statements, highlighting how crucial accurate disclosure is to making well-informed decisions.
Conservatism
In accounting, the conservative principle supports cautious assessment and judgement. In order to ensure a balanced and cautious approach, it encourages accountants to choose methods that minimise overstating assets and income while understating liabilities and expenses when faced with uncertainty.
Comparability
Comparability makes it possible to analyse and contrast financial data from different companies or time periods. This feature gives stakeholders the ability to compare financial performances, which facilitates decision-making by offering a framework for assessment.
Upholding Consistency
The practice of using the same accounting procedures and policies throughout accounting periods is emphasised by consistency. By promoting consistency and dependability in financial reports, this approach enables stakeholders to make wise decisions over time.
The trio of Financial Statement :
Income :
This statement summarises the earnings, costs, and net profit or loss for a given time period for a business. It provides an overview of operational performance by displaying the profit margin after deducting expenses.
Balance:
The balance sheet, a fundamental component of financial reporting, provides a thorough overview of the assets, liabilities, and equity of a business at a specific point in time. It draws attention to the organization’s overall health and financial situation.
Cash Flows :
The inflow and outflow of cash and cash equivalents within the company are shown in this crucial statement. It illustrates the ways in which the company’s financing, investments, and operations affect its liquidity.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's):
A formal report outlining a company’s financial situation at a given point in time is called a financial statement. It is divided into three parts: equity, liabilities, and assets.
Investors can quickly assess a company’s financial health by looking at its financial statements. They make cash flow, profitability, and overall financial stability clear.
The income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and statement of shareholders’ equity are among the most important financial statements.
Identification, recording, necessary adjustments, post-entry, creation of the income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, statement of shareholders’ equity, and closing of the business are all required to prepare financial statements.
Accounting standards, such as IFRS and GAAP, provide guidelines that guarantee the dependability, consistency, and comparability of financial statements between companies and time periods. Respecting these guidelines is essential for maintaining stakeholder trust and legal compliance.
Financial statement analysis is essential even though it isn’t a direct preparation step. It entails analysing these statements to determine the financial stability of an organisation. Ratio and trend analysis are two techniques that help stakeholders make decisions by assisting in the evaluation of performance, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency.
In order to guarantee correctness, dependability, and adherence to accounting standards, auditors carefully examine financial statements, documentation, and internal controls. Their published opinions support stakeholder trust and adherence to guidelines by reaffirming the degree of confidence in the statements’ justice and accuracy.

